Smart corporate reflexes combine blockchain, edge IoT and Value-Stream-as-a-Service.
Part I explored autonomy for the Enterprise-In-Motion, including the value of self-optimization and self-healing, autonomic computing, and critical automation capabilities. Key enablers include Digital Process Automation (DPA) and artificial intelligence, the nervous system.
This Part II focuses on three additional enablers for autonomy: Blockchains, edge computing, and Value-Stream-As-A-Service. Autonomy emanates from their combined transformational potential.
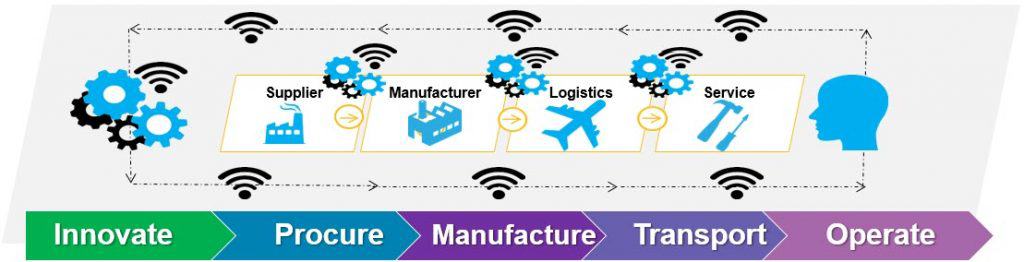
To set the stage for the Autonomy in the Enterprise-In-Motion, consider a product innovation and production use case. Multiple enterprises and organizations need to collaborate to achieve robust outcomes. The entire end-to-end Value stream needs to be autonomic: self-optimizing and self-healing when there are delays or quality issues, for instance. This needs to happen on the cloud involving geographically distributed enterprises.
Blockchain and DAOs for Autonomy
Blockchain is very much a revolution. It is the engine that empowers the emergence of the Internet of Value – extending the traditional Internet of Information and the Internet of Things. Ripple’s description of Internet of Value is quite good: “Value to be exchanged as quickly as information.” The speed and disintermediated exchange of value has tremendous implications for the Enterprise-In-Motion.
Blockchain is the foundation of cryptocurrencies. These, in turn, facilitate the emergence of new economies and disruptive models of value exchanges across enterprises and countries (in a supply chain), for example. In addition to the peer-to-peer, decentralized and disintermediated recording of transactions, blockchains also execute Smart Contracts. Smart contracts are the rules and mutual agreements between parties that get executed in the blockchain.
The applications are many. Through peer-to-peer transactions without intermediaries, blockchain technology lets individuals and organizations easily exchange digital money and execute business contracts between trading partners. Take the generic manufacturing value stream example above, which at its core reflects the capabilities of Adaptive Digital Factories. Each of the milestones in the end-to-end value stream can involve blockchains. Here are few possibilities:
- Mobile, Additive and Social Manufacturing: Participating in end-to-end production with 3D printing, together with social and additive manufacturing. Blockchain can be used for the exchange of components, payments, and tracking in the supply chain.
- Logistics and Transportation: Supply chain is one of the most robust applications of blockchain – as value and tracking can be traced on immutable ledgers across enterprises in potentially different countries.
- Servicing and Operations: Provisioning the best field service technicians and continuous monitoring for optimizations can leverage blockchain – for smart contracts, payments, and recording of operational work on the decentralized ledger.
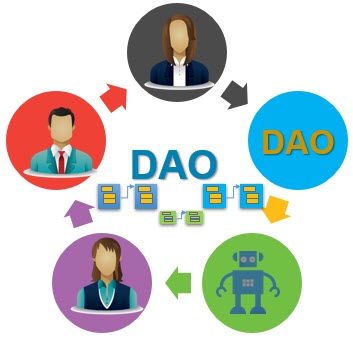
Moreover, blockchain enables decentralized applications and, even more importantly, Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAO). Blockchain within enterprises can also promote alternative flat organizational patterns. Applications built on blockchain can allow organizations to execute smart decisions (via smart contracts executing on the blockchain) such as proposals, recommendations, asset allocations, votes, etc. These can involve employees as well as partners and even customers across multiple organizations.
The governance, constitution, bylaws and operation of a DAO uses smart contracts executing on the blockchain. A DAO can involve human participants, AI, robots or other DAOs. The potential is to digitally transform traditional siloed business practices with potentially decentralized agile organizations. In this way, blockchain could become a critical contributor for decentralized governance. DAO allows participation by all shareholders, employees or other stakeholders to quickly agree and vote on decisions. Since actual code is executed for running the organization, it leaves little to the imagination for the interpretation of the governing policies.
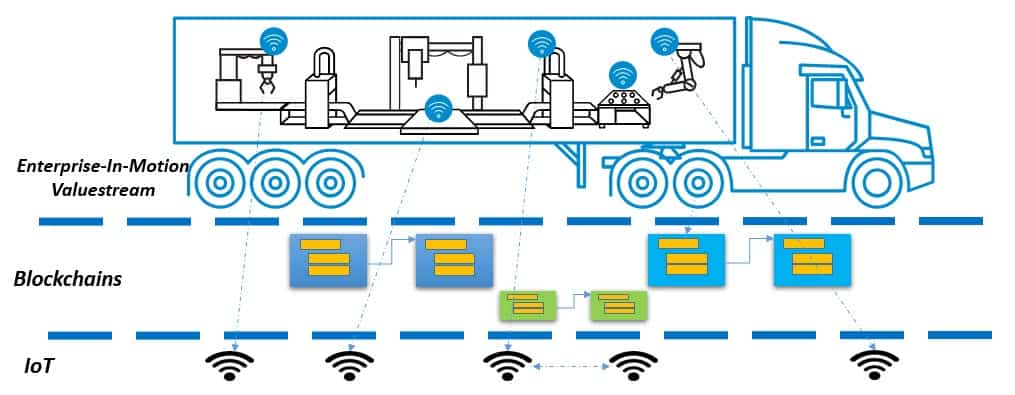
IoT Edge Computing
As illustrated above, IoT connected devices are at the edges – or lowest level – of the Enterprise-In-Motion ecosystem. The Internet of Things (IoT) and the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) are significant contributors to digital transformation.
When it comes to autonomic IoT, the emerging connected devices trend is edge computing. Increasingly, business logic and AI models are executing at the IoT edges. The actuators and sensors of connected devices often leverage gateways to connect to the Cloud. Connected devices and gateways are becoming ever more powerful in storage, computation, and networking optimizations.
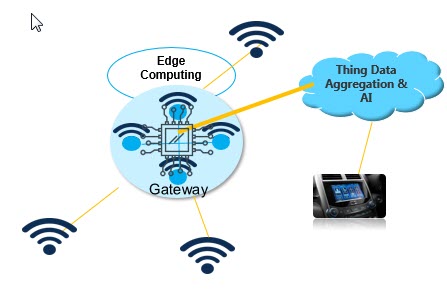
Edge computing offers several pragmatic advantages. First, the approach will reduce the network traffic of connected devices – some of which can generate several terabytes of data daily; for instance, 4 TB of data per day for autonomous cars.
With a traditional cloud approach (i.e. transmitting Thing Data and then processing on the cloud) vast volumes must be sensed and transferred to the cloud. Even more importantly, there is a latency from the time a pattern is detected to the time the necessary – sometimes critical – action is sent back to the device for execution. The more this data is processed through executing AI models at the edges, the better for the network bandwidth and storage. The more that data is analyzed and processed at the edges, the better. And the more devices become intelligent and self-optimizing, all the better.
Speed of responsiveness is also critical. Edge computing avoids the latencies of transmitting the data to the Cloud, analyzing, discovering AI models and then executing the needed action. Edge computing lets devices take immediate action. In other words, edge computing is faster and more optimized.
Of course, the filtered data from various connected edge devices still gets sent to the cloud. Data from different connected devices is combined with enterprise data to detect AI models through a plethora of Machine Learning algorithms. The discovered intelligence is then sent back to the devices for execution. Thus, the intelligence of the connected edge device computing emanates from the real-time detection and execution of the AI models on the device, as well as from the downloaded intelligence from the cloud. Autonomy needs both.
Analytics drives business value in IoT solutions, but not all analytics needs to be in the cloud. In addition to the emerging reference architecture stack and the insight-to-action of Thing Data, in a robust Enterprise-In-Motion architecture the autonomic business value is achieved through end-to-end digitization and automation of value streams via Digital Process Automation.
For many of manufacturing milestones, edge computing offers concrete advantages:
- Supply Chain Optimizations: Edge computing can optimize and route movement of material or manufactured products executing in transit. The computing self-optimizes through execution of AI models that have learned over time as well as on the transportation device edge analytics and computing.
- Digital Prescriptive Maintenance (DPM): Maintenance is the killer application of IoT. However, the road to success for DPM is achieved through Digital Process Automation. DPA itself incorporates the execution of AI models. The closer this execution of maintenance practices to the edges the better – for the reasons mentioned above (reducing data traffic and enhancing the speed of responsiveness). Increasingly the Industry 4.0 manufacturing shop-floors involve connected machines, robots, and devices. The self-optimizing and self-healing operations of these machines are critical. Typically the manufactured products are themselves connected devices and they too need digital prescriptive maintenance!
Value-Stream-As-A-Service for Autonomy
Which brings us to the last – but perhaps most important – enabler. The Enterprise-In-Motion will achieve its autonomous objectives in the context of end-to-end value streams executing on the cloud.
As discussed in the VSaaS article, Value-Stream-As-A-Service is a new model for collaboration, involving multiple enterprises or business units. With the proper governance through Digital Process Automation, together with Internet of Value capabilities, it enables a marketplace of end-to-end solutions that will allow solution providers to plug in as participants in the value streams.
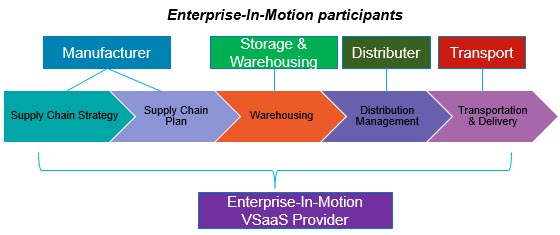
Now here is the critical challenge: a VSaaS is only as strong as the weakest enterprise participating in its value proposition. Using the generic manufacturing example, the entire innovative manufacturing process depends on the self-optimization and self-healing of each participant. So if a supplier enterprise cannot provision material or parts in time or on a par with the best critical-to-quality measures, the entire production will suffer.
In reality, VSaaS is an extended Enterprise-In-Motion. As defined in Service Oriented Enterprisesin an extended enterprise “various applications, repositories, and even roles or organizations appear to be well aggregated and integrated, while staying loosely coupled and independent… The output of one application, such as the blueprint of a product component [can be] the input of another application, such as an automated manufacturing plant… So the enterprise is extended: it includes parts and services obtained sometimes from organizations that are thousands of miles away.”
The extended enterprise through VSaaS can actually be realized via a DAO, or even by an ecosystem of multiple DAOs. The extended Enterprise-In-Motion on the DAO can potentially self-optimize and self-heal at a much faster speed by carrying out autonomous enterprise decisions with blockchain smart contracts executing autonomic policies. These can be either completely automated or involve participants in the DAO (e.g. voting). Autonomy is achieved through end-to-end Value streams, enabled through blockchains as needed. DAO provides a robust peer-to-peer infrastructure for trust, and actual extended Enterprise-In-Motion business logic can execute in the blockchain.
End-to-end visibility and optimized collaboration between various stakeholders and trading partners are tremendously empowering advantages of VSaaS for autonomy. The other obvious advantage is the potential to innovate and create new service offerings from the VSaaS solutions – for financial self-optimizations of the extended Enterprise-In-Motion.
Autonomic Conclusions …
How far are we from Autonomy for the Enterprise-In-Motion? Will it happen?
Each of the catalysts discussed here (AI, DPA, Blockchain, IoT Edge, VSaaS) has its own challenges and risks. At the end of the day, an Enterprise-In-Motion is a complex system that responds to stimuli. Complexity increases exponentially with extended Enterprise-In-Motion. Autonomic behavior becomes increasingly difficult.
Some will argue we have been down this path before. “Real-time enterprise,” “adaptive enterprise,” “digital enterprise,” or “service-oriented enterprise” – all have attempted to capture the notion of autonomic in-motion behavior, with varying success.
Yet many enterprises remain archaic. Legacy organizational structures and behaviors have survived decades – if not centuries – with layers of management control and power-driven bureaucratic practices that suffocate innovation.
Ultimately, the digital era, and more importantly, Gen Y (Millennials) and Gen Z demand autonomic behavior. The latter are the face of unstoppable cultural mega-trends exerting tremendous impact on innovation – challenging hierarchical, centralized control-driven organizations with more innovative, flat models that empower participants. The digital technologies discussed here are just enablers of cultural trends rapidly transforming all demographics. Culture is always more important and impactful than pure digital technologies, as impressive as the latter may be.
The change is already in motion, and accelerating quickly.