How does the Internet of Things (IoT) differ from the traditional Internet? Here, RTInsights International Technology Editor Opher Etzion summarizes the main differences between the two.
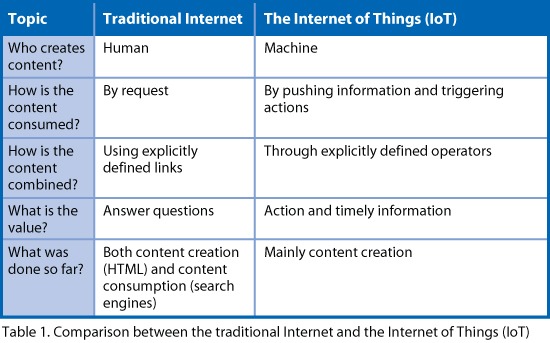
The first and most grasped difference between the traditional Internet and the IoT is the identity of the content creation (as noted in Table 1 below). However, there are several other notable differences.
For example, the content in the traditional Internet is consumed by request; that is, one has to ask a query, issue a search or send a request for a web service in order to consume the content. On the contrary, in the IoT, the content is typically consumed through pushing the technology as a notification or triggering an action when a situation of interest is detected. In many cases, the consumption means combining data from different sources. This is true for the traditional Internet as well as the IoT.
In the traditional Internet, the connection is done through physical links between web pages. In the IoT, the combination of data is required for situation detection. This is manifested in the combining of data in the form of context-based event patterns in which some of the data determines the context and other determines the pattern itself.
There is also a difference in the value to the consumer. In the traditional Internet, the value resides in answering a question that is posed by the consumer, in many cases when searching for information or activating services. In the IoT, the value is timely action or notification based on detected situations.
This brings us to comparing the state of the art in both areas. The traditional Internet is a mature technology; it has standards in various areas and search engines that one can communicate with using natural languages. The net result is that the consumption of the traditional Internet can be done by everybody without the need of any technical skills.
But in the IoT domain, the situation is quite different. The standardization effort is only in its first phases, thus, the data integration is done ad hoc and requires skilled programmers in order to implement an application.
As for the logic of situation detection, imagine that, instead of using search engines, every Internet query would have required the construction of Structured Query Language (SQL) queries. Under this scenario, Internet use would have been restricted only to those who can write SQL queries, which is a very small portion of current Internet consumers.
In the IoT domain, the situation is even worse. The languages that exist are even more low-level relative to SQL and require a good understanding of the particular semantics of the language. As a result, personalization of the application becomes, in many cases, practically impossible.
In my next article, I will discuss some possible solutions for the personalization aspect.
![Sponsored Resource: Enhancing Intelligent Real-Time Monitoring with Streaming Analytics Using Real-Time Digital Twins [Download Now]](https://no-cache.hubspot.com/cta/default/8019034/68465e27-def5-49e0-953f-88df4c33b69c.png)